Ways To Identify Heel Spur

Overview
Heel spur (Calcaneal spur) is a bonny outgrowth of the heel bone which is pointy in shape. It?s a calcium deposit that happens under the heel bone. In some cases, the protrusion due to heel spur can extend up to half inch and can be seen in X rays. Generally it is painless but sometimes it may result in heel pain. Heel spur that occur under the sole of the foot or the planter area is associated with plantar fasciitis. That is frequently associated with plantar fasciitis as they have many similarities.
Causes
Heel spurs form in some patients who have plantar fasciitis (PLAN-tar fash-ee-I-tis), and tend to occur in patients who have had the problem for a prolonged period of time. While about 70 percent of patients with plantar fasciitis have a heel spur, X-rays also show about 50 percent of patients with no symptoms of plantar fasciitis also have a heel spur.

Symptoms
Although it may take years to become a problem, once it appears, it may cause considerable suffering. Because of proximity to the tendons, the spur is a source of continuous painful aching. The sensation has been described as "a toothache in the foot." When you place your weight on the heel, the pain can be sufficient to immobilize you.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of a heel spur can be done with an x-ray, which will be able to reveal the bony spur. Normally, it occurs where the plantar fascia connects to the heel bone. When the plantar fascia ligament is pulled excessively it begins to pull away from the heel bone. When this excessive pulling occurs, it causes the body to respond by depositing calcium in the injured area, resulting in the formation of the bone spur. The Plantar fascia ligament is a fibrous band of connective tissue running between the heel bone and the ball of the foot. This structure maintains the arch of the foot and distributes weight along the foot as we walk. However, due to the stress that this ligament must endure, it can easily become damaged which commonly occurs along with heel spurs.
Non Surgical Treatment
Diathermy treatment uses an electrical current to produce heat that sedates the inflamed tissues. The ultrasound device sends sound waves into the heel and sets up a massaging action that stimulates blood circulation. Treatment with a whirlpool bath involves placing the foot directly into the jetting stream. Orthopedic molds and appliances, such as orthotics, are designed by foot specialists for use inside the shoe to eliminate irritation to the heel when the patient stands or walks. When those appliances are used, the spur (in effect) floats on air. At the same time, the body's weight is transferred forward from the tender spot.
Surgical Treatment
Surgery is used a very small percentage of the time. It is usually considered after trying non-surgical treatments for at least a year. Plantar fascia release surgery is use to relax the plantar fascia. This surgery is commonly paired with tarsal tunnel release surgery. Surgery is successful for the majority of people.
Bursitis Foot Pain Signs Or Symptoms
Retrocalcaneal bursitis is the inflammation of the retrocalcaneal bursa, which is located behind the heel bone, also known as the calcaneal bone (hence the name retrocalcaneal). The retrocalcaneal bursa is a thin, slippery, fluid-filled sac that serves as a both a cushion and lubricant between the heel bone and the Achilles tendon. Inflammation of the retrocalcaneal bursa usually results from irritation of the bursa. This irritation may be due to certain activities, an underlying health condition such as arthritis, or an abnormality of the foot, such the development of a boney prominence on the calcaneal bone, called a Haglund's deformity.
Causes
Bursitis occurs when the bursae become irritated or infected, often causing pain on movement. When infection is involved, medical intervention is necessary to fight the underlying infection and prevent it from spreading, when infection is not involved, prompt medical attention can prevent the condition from becoming worse over time.
Symptoms
A person with bursitis can have one or more of the symptoms below. Pain, the pain increases with movement or pressure. Tenderness is felt even without movement. Swelling. Loss of movement. If the bursitis is caused by an infection it is called Septic Bursitis. The patient with septic bursitis may have the following additional symptoms. Fever. The affected area is red. The affected area feels hot when touched.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of heel bursitis can be made by your health practitioner and is based on the following. Assessing the location of the pain by palpating the back of the heel. Assessment of any inflammation at the back of the heel. Assessment of biomechanics and foot function. Ultrasound or MRI can reveal inflammation of the retro calcaneal bursa.
Non Surgical Treatment
Relieving the symptoms of bursitis initially focuses on taking the pressure off the bursa. This can be done with proper cushioning, inserts, or footwear but may require surgery if it is a bone formation problem (i.e. Huglund's Deformity). If your bursitis is caused by an infection (septic bursitis), the doctor will probably drain the bursa sac with a needle and prescribe antibiotics to treat the infection.
Surgical Treatment
Surgery is rarely need to treat most of these conditions. A patient with a soft tissue rheumatic syndrome may need surgery, however, if problems persist and other treatment methods do not help symptoms.
Hammer Toe Treatment In The Home
 Overview
Overview
hammertoes is often a harmless and painless condition. Although the toe may be curled permanently, hammertoe should not cause any long-term problems other than a more difficult time finding shoes that fit. If hammertoe is treated and preventive measures are followed, the condition should not return. Wearing tight or constricting shoes can cause hammertoe to return.
Causes
Claw, hammer and mallet toe are most commonly caused by wearing high heels or ill-fitting shoes that are too tight e.g. narrow toebox. If shoes like this are worn for long periods, the foot is held in a slightly bent position and gradually over time, the muscles tighten and shorten. If this continues for long enough, then the muscles become so tight that even when shoes are removed, the toe is still held in the bent position. Another common cause is Morton?s Toe, where the second toe is longer than the big toe. In this case, the second toe is commonly squashed into a shoe into an unnaturally bent position.
 Symptoms
Symptoms
Symptoms include sharp pain in the middle of the toe and difficulty straightening the toe. People with hammertoe may also develop blisters, which are fluid-filled pockets of skin, because the bent toe is likely to rub against the inside of a shoe. This increased friction may also lead to calluses, which are areas of thickened skin, and corns, which are hard lumps that may form on or between toes. Symptoms may be minor at first, but they can worsen over time.
Diagnosis
Your doctor is very likely to be able to diagnose your hammertoe simply by examining your foot. Even before that, he or she will probably ask about your family and personal medical history and evaluate your gait as you walk and the types of shoes you wear. You'll be asked about your symptoms, when hammertoes they started and when they occur. You may also be asked to flex your toe so that your doctor can get an idea of your range of motion. He or she may order x-rays in order to better define your deformity.
Non Surgical Treatment
Your doctor may prescribe some toe exercises that you can do at home to stretch and strengthen the muscles. For example, you can gently stretch the toes manually. You can use your toes to pick things up off the floor. While you watch television or read, you can put a towel flat under your feet and use your toes to crumple it. Finally, your doctor may recommend that you use commercially available straps, cushions or nonmedicated corn pads to relieve symptoms. If you have diabetes, poor circulation or a lack of feeling in your feet, talk to your doctor before attempting any self-treatment.
Surgical Treatment
Several surgical procedures are available to the podiatric physician. For less severe deformities, the surgery will remove the bony prominence and restore normal alignment of the toe joint, thus relieving pain. Severe hammertoes, which are not fully reducible, may require more complex surgical procedures. Recuperation takes time, and some swelling and discomfort are common for several weeks following surgery. Any pain, however, is easily managed with medications prescribed by your podiatric physician.
 Prevention
Prevention
The easiest way to avoid hammertoe is to wear shoes that fit properly. Orthopaedic surgeons and podiatrists recommend shoes that have roomy toe boxes, which give the toes plenty of space to flex. Shoes that fit well should also cushion the arch in the middle of the foot. This helps to distribute the weight of the body evenly across the bones and joints of the foot. The size and shape of a foot can change with age, and many people inadvertently wear the wrong size shoe. Podiatrists recommend having your feet measured regularly to ensure that your shoes fit properly.
Is Hammer Toe Debilitating
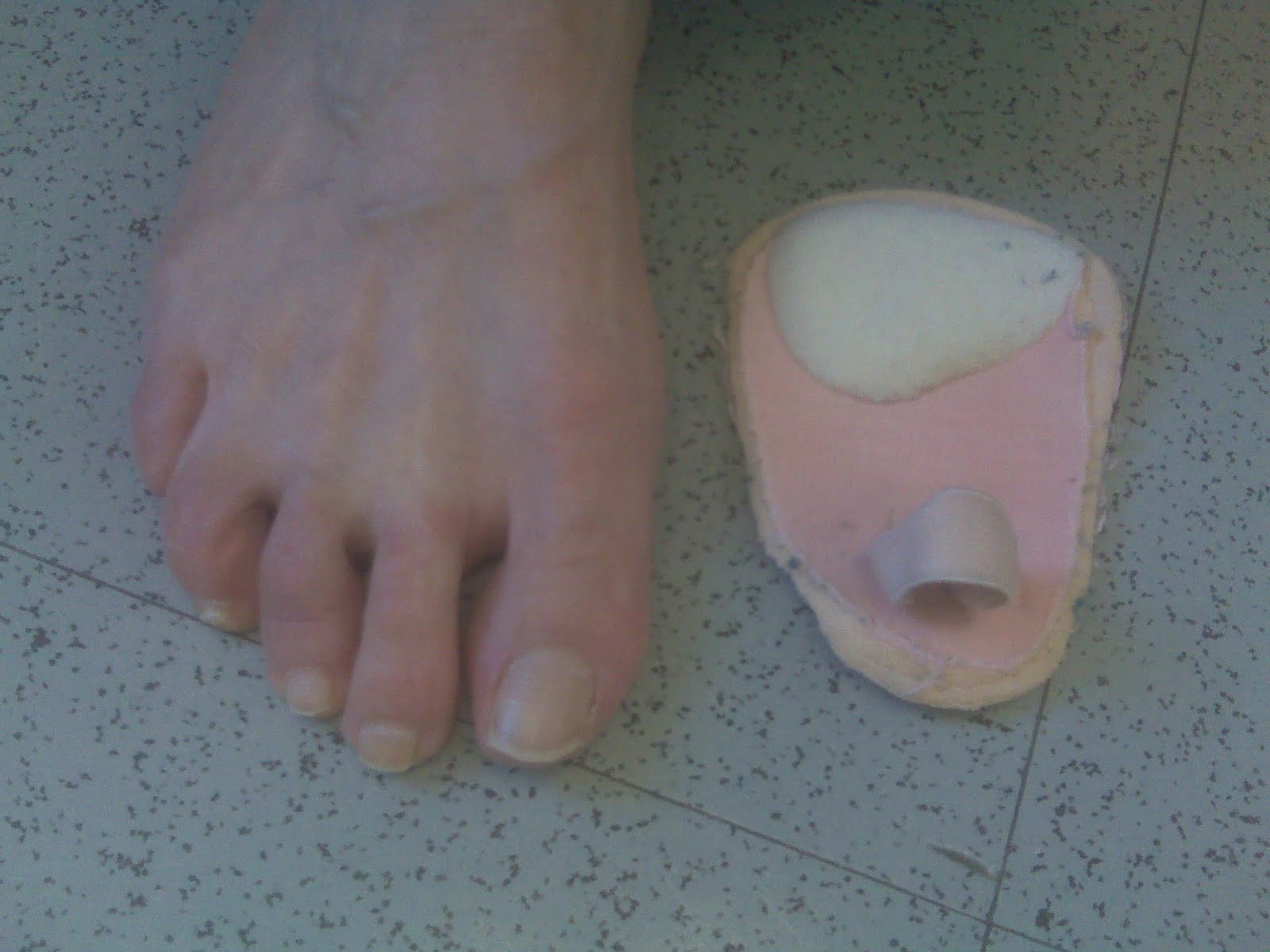 Overview
Overview
The term, hammertoe, is commonly used as a general classification for any condition where the toe muscle weakens, causing digital contracture, and resulting in deformity, a digital contracture like this can actually be a hammertoe, claw toe or mallet toe, depending on which joints in the toe are contracted. Clawtoes are bent at the middle and end joints, while hammertoes are bent at the middle joint only. When it?s mallet toe, the joint at the end of the toe buckles. The skin near the toenail tip develops a painful corn that can eventually result in an ulcer. Doctors further categorize all forms of hammertoe based on whether the affected toe is flexible, semi-rigid or rigid. The more rigid the toe, the more pain it will cause.
Causes
Ill-fitting shoes or a muscle imbalance are the most common causes of Hammer Toe. If there is an issue with a muscle in the second, third or fourth toes preventing them from straightening, Hammer Toe can result. If one of these toes is bent long enough in one position, the muscles tighten and cannot stretch out. Left untreated, surgery may be required. Women are especially prone to developing Hammer Toe because of their shoes. Hammer Toe results from shoes that don?t fit properly. Shoes that narrow toward the toe, pushing smaller toes into a bend position for extended periods of time. High heels that force the foot down into a narrow space, forcing the toes against the shoe, increasing the bend in the toe.
 Symptoms
Symptoms
Here is a look at some of the symptoms hammertoe can cause. They include hammer-like or claw-like appearance of the toe. Pain when walking or moving the foot. Difficulty moving the toe. Corns may form on top of the toe. Callus may form on the sole of the foot. During the initial stages, you may be able to manually straighten your toe. This is called a flexible hammertoe. But as time passes, the toe will not move as easily and will continue to look like a hammer. Pressure and irritation over the joint can cause a blister to develop and become a corn over time. These corns have the potential to become infected and cause additional symptoms such as redness, bleeding, and difficulty wearing shoes and socks. Corns are the main cause of pain when hammertoes are developing.
Diagnosis
Most health care professionals can diagnose hammertoe simply by examining your toes and feet. X-rays of the feet are not needed to diagnose hammertoe, but they may be useful to look for signs of some types of arthritis (such as rheumatoid arthritis) or other disorders that can cause hammertoe. If the deformed toe is very painful, your doctor may recommend that you have a fluid sample withdrawn from the joint with a needle so the fluid can be checked for signs of infection or gout (arthritis from crystal deposits).
Non Surgical Treatment
If the toes are still mobile enough that they are able to stretch out and lay flat, the doctor will likely suggest a change of footwear. In addition, she may choose to treat the pain that may result from the condition. The doctor may prescribe pads to ease the pain of any corns and calluses, and medications ranging from ibuprofen to steroid injections for the inflammation and pain. Other options for non-surgical treatments Hammer toes include orthotic devices to help with the tendon and muscle imbalance or splinting to help realign the toe. Splinting devices come in a variety of shapes and sizes but the purpose of each is the same: to stretch the muscles and tendon and flatten the joint to remove the pain and pressure that comes from corns.
Surgical Treatment
In advanced cases in which the toe has become stiff and permanently bent, the toe can be straightened with surgery. One type of surgery involves removing a small section of the toe bone to allow the toe to lie flat. Surgery for hammertoe usually is classified as a cosmetic procedure. Cosmetic foot surgeries sometimes result in complications such as pain or numbness, so it's better to treat the problem with a shoe that fits properly.
Is Over-Pronation
The anatomy of a normal foot allows for both to occur at the same time. Approximately 30% of the population have a normal foot. The remainder of people either overpronate (95% of abnormal feet) or oversupinate (5% of abnormal feet). The important thing to know is that all feet pronate and supinate, but abnormal feet do one of these things too much or at the wrong time. When the foot overpronates or oversupinates, several foot ailments can develop.

Causes
A common cause of pronation is heredity - we can inherit this biomechanical defect. The second most common cause is due to the way our feet were positioned in the uterus while we were developing; this is called a congenital defect. In either instance, the following occurs in our feet during our development.
Symptoms
Because overpronation affects the entire lower leg, many injuries and conditions may develop and eventually cause problems not only in the leg and foot, but also the knee, hips and lower back. Pain often begins in the arch of the foot or the ankle. Blisters may develop on the instep, or on the inside edge of the heels. As overpronation continues and problems develop, pain will be felt elsewhere, depending on the injury.
Diagnosis
The best way to discover whether you have a normal gait, or if you overpronate, is to visit a specialty run shop, an exercise physiologist, a podiatrist or a physical therapist who specializes in working with athletes. A professional can analyze your gait, by watching you either walk or run, preferably on a treadmill. Some facilities can videotape your gait, then analyze the movement of your feet in slow-motion. Another (and less costly) way is to look at the bottom of an older pair of run shoes. Check the wear pattern. A person with a normal gait will generally see wear evenly across the heel and front of the shoe. A person who overpronates will likely see more wear on the OUTside of the heel and more wear on the INside of the forefoot (at the ball). A person who supinates will see wear all along the outer edges of the shoe. You can also learn about your gait by looking at your arches. Look at the shape your wet feet leave on a piece of paper or a flat walking surface.

Non Surgical Treatment
Overpronation is a term used to describe excessive flattening of the plantar arch. Pronation is a normal part of our gait (the way we walk), and it comprises three movements: dorsiflexion, eversion, and abduction. Dorsiflexion is the upward movement of the foot, eversion describes the foot rolling in, and abduction is ?out toeing,? meaning your toes are moving away from the midline of your body. When these three motions are extreme or excessive, overpronation results. Overpronation is very common in people who have flexible flat feet. Flatfoot, or pes planus, is a condition that causes collapse of the arch during weight bearing. This flattening puts stress on the plantar fascia and the bones of the foot, resulting in pain and further breakdown.
Prevention
Many of the prevention methods for overpronation orthotics, for example, can be used interchangeably with treatment methods. If the overpronation is severe, you should seek medical attention from a podiatrist who can cast you for custom-made orthotics. Custom-made orthotics are more expensive, but they last longer and provide support, stability, and balance for the entire foot. You can also talk with a shoe specialist about running shoes that offer extra medial support and firm heel counters. Proper shoes can improve symptoms quickly and prevent them from recurring. Surgery can sometimes help cure and prevent this problem if you suffer from inherited or acquired pes planus deformity. Surgery typically involves stabilizing the bones to improve the foot?s support and function.
What Are The Causes Of Severs Disease?
Foot pain is not only limited to grown-ups. Often, healthy and active children will complain of pain in one or both heels shortly after running, engaging in sports or even walking. The pain is centered at the back of, or under the heel. The cause of heel pain in children is usually a condition called calcaneal apophysitis, normally reported by 8 to 14 year olds.
Causes
The most common of the Sever?s disease causes is when the heel bone grows more rapidly than the muscles and tendons in the leg. The muscles and tendons become tight and put additional stress on the growth plate in the heel. When this happens, the growth plate begins to swell, becomes tender, and the child will essentially begin to feel one or more Sever?s disease symptoms. It can occur in any child as they grow, but there are some common Sever?s disease causes and risk factors that make a child more prone to the condition. They include participation in sports and other activities that put pressure on the heel, such as basketball, track, and gymnastics. A pronated foot, which makes the Achilles tendon tight, increasing the strain on the growth plate of the heel. An arch that is flat or high, affecting the angle of the heel. Short leg syndrome, when one leg is shorter than the other, causing the shorter leg to pull more on the Achilles tendon in order to reach the ground. Obesity puts extra weight on the growth plate, which can cause it to swell.
Symptoms
Typically, the sports injury occurs where the achilles tendon attaches to the bone. The epiphyseal growth plate is located at the end of a developing bone where cartilage turns into bone cells. As the growth center expands and unites, this area may become inflamed, causing severe pain when both sides of the heel are compressed. There is typically no swelling and no warmth, so it?s not always an easy condition to spot. The child usually has trouble walking, stiffness upon waking, and pain with activity that subsides during periods of rest.
Diagnosis
Your podiatrist will take a comprehensive medical history and perform a physical examination including a gait analysis. The assessment will include foot posture assessment, joint flexibility (or range of motion), biomechanical assessment of the foot, ankle and leg, foot and leg muscle strength testing, footwear assessment, school shoes and athletic footwear, gait analysis, to look for abnormalities in the way the feet move during gait, Pain provocation tests eg calcaneal squeeze test. X-rays are not usually required to diagnose Sever?s disease.
Non Surgical Treatment
There is nothing you can do to stop severs disease. It will stop when you finish growing. However the following will help to relieve the symptoms. Rest. Cut down on the time you spend playing sport until the pain has gone. Avoid sports that involve a lot of running or jumping. Swimming can be a useful alternative. Ice the affected area for ten to 15 minutes, especially after activity. Make sure you protect the skin by wrapping the ice in a towel. Elevate (raise) the leg when painful and swollen especially after sports. Pain relieving medication may reduce pain and swelling, but you need to discuss options with a pharmacist or GP. Always wear shoes. Avoid activities in bare feet. Choose a supportive shoe with the laces done up.
Prevention
To reduce the risk of heel pain or sore heels from Sever?s Disease. Only wear properly fitting shoes. A lace up shoe with a firm heel counter. Stretch calf and foot before exercising or playing sports. Properly taping the foot provides excellent protection and immediate pain relief. Wear shoe inserts or an over-the-counter orthotic. If the problem persists, consult your foot doctor.
Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction Orthotics
Overview
Adult-acquired flatfoot or collapsed arch occurs because the large tendon on the inside of the ankle - the posterior tibial tendon - becomes stretched out and no longer supports the foot?s arch. In many cases, the condition worsens and and the tendon thickens, becoming painful, especially during activities. Flatfoot or collapsed arch is also known as posterior tibial tendon dysfunction. This condition is different than having flat feet since birth (known as congenital flatfoot), although sometimes these patients develop similar symptoms and require similar treatments. 
Causes
Overuse of the posterior tibial tendon is often the cause of PTTD. In fact, the symptoms usually occur after activities that involve the tendon, such as running, walking, hiking, or climbing stairs.
Symptoms
Posterior tibial tendon insufficiency is divided into stages by most foot and ankle specialists. In stage I, there is pain along the posterior tibial tendon without deformity or collapse of the arch. The patient has the somewhat flat or normal-appearing foot they have always had. In stage II, deformity from the condition has started to occur, resulting in some collapse of the arch, which may or may not be noticeable. The patient may feel it as a weakness in the arch. Many patients initially present in stage II, as the ligament failure can occur at the same time as the tendon failure and therefore deformity can already be occurring as the tendon is becoming symptomatic. In stage III, the deformity has progressed to the extent where the foot becomes fixed (rigid) in its deformed position. Finally, in stage IV, deformity occurs at the ankle in addition to the deformity in the foot.
Diagnosis
The history and physical examination are probably the most important tools the physician uses to diagnose this problem. The wear pattern on your shoes can offer some helpful clues. Muscle testing helps identify any areas of weakness or muscle impairment. This should be done in both the weight bearing and nonweight bearing positions. A very effective test is the single heel raise. You will be asked to stand on one foot and rise up on your toes. You should be able to lift your heel off the ground easily while keeping the calcaneus (heel bone) in the middle with slight inversion (turned inward). X-rays are often used to study the position, shape, and alignment of the bones in the feet and ankles. Magnetic resonance (MR) imaging is the imaging modality of choice for evaluating the posterior tibial tendon and spring ligament complex.
Non surgical Treatment
Options range from shoe inserts, orthotics, bracing and physical therapy for elderly and/or inactive patients to reconstructive surgical procedures in those wishing to remain more active. These treatments restore proper function and alignment of the foot by replacing the damaged muscle tendon unit with an undamaged, available and expendable one, lengthening the contracted Achilles tendon and realigning the Os Calcis, or heel bone, while preserving the joints of the hindfoot. If this condition is not recognized before it reaches advanced stages, a fusion of the hindfoot or even the ankle is necessary. Typically this is necessary in elderly individuals with advanced cases that cannot be improved with bracing. 
Surgical Treatment
Although non-surgical treatments can successfully manage the symptoms, they do not correct the underlying problem. It can require a life-long commitment to wearing the brace during periods of increased pain or activity demands. This will lead a majority of patients to choose surgical correction of the deformity, through Reconstructive Surgery. All of the considerations that were extremely important during the evaluation stage become even more important when creating a surgical plan. Generally, a combination of procedures are utilized in the same setting, to allow full correction of the deformity. Many times, this can be performed as a same-day surgery, without need for an overnight hospital stay. However, one or two day hospital admissions can be utilized to help manage the post-operative pain. Although the recovery process can require a significant investment of time, the subsequent decades of improved function and activity level, as well as decreased pain, leads to a substantial return on your investment.